Your donation will support the student journalists of North Cobb High School. Your contribution will allow us to purchase equipment and cover our annual website hosting costs.
Learning styles in school
November 25, 2020
At the start of each school year, students will take “get to know you” quizzes given to them by their teachers. A portion of teachers will write “What is something I can do to help you learn” as the last question. To expand upon this subject, teachers may even give students a learning style quiz to determine how they best understand and absorb information. Students can have three different learning styles or even a mixture of two or more. The learning styles include Visual, Auditory, and Experiential.
As students progress through grades k-12 it becomes less likely that students with certain learning styles will understand the class material. For example, in the third-grade teachers will play songs to teach new topics, but in ninth grade those things become impractical. As the learning material and teaching methods change, students’ learning styles either start to shift or the students will start to need extra help.
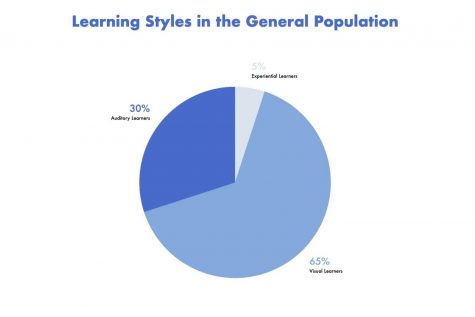
Visual learners, the most common learning style, take up about 65% of the population. They learn best by reading things, seeing diagrams and pictures. These learners can easily follow through instruction manuals but verbal instructions may cause confusion.
Andrea Drake, 9th grade English teacher at NC with nine years of experience teaching at the school. When teaching she likes to use the Smartboard in her classroom to have the lesson clear for each student to see. Mrs. Drake also likes to include either blank or guided notes that students will take in her class.
“Additionally, graphic organizers and worksheets are used to help these students visualize their writing assignments. I also frequently try to design assignments that allow students to answer in using a visual instead of just a written assignment,” Drake said.
Carmen Willison, a 3rd-grade teacher at Chalker elementary school, has worked at Chalker for three years but has taught for a total of twenty-two years. For visual learners, Mrs. Willison likes to use anchor charts with drawings to help these students visualize the lesson.
“I use lots of colors. Examples, lists, diagrams, images, and other or all types of information can be added to large chart paper and posted for students to use,” Willison said.
Auditory learners “learn by ear” and absorb information by listening to instruction. Auditory learners typically enjoy the musical arts and they might even create songs to help them learn. They can easily memorize song lyrics, but they could possibly not understand a PowerPoint presentation. These learners take up about 30% of the population.
When it comes to Auditory learning students, Mrs. Drake will include clips from movies and different audios while stopping frequently to let students ask questions. She will also put students into small groups to discuss different topics and will occasionally have the students participate in a Socratic seminar.
“When [engaging with and] providing instruction for auditory learners, I use videos from a website called Flocabulary and other similar internet-based learning sources. These types of videos teach content with catchy songs,” Willison said.
Experiential, Kinesthetic or “hands-on learners”, prefer learning with movement and interactive activities to create an experience they can remember. Kinesthetic learners might like to work with clay, participate in sports or talk with their hands. These students learn by doing. On the other hand, sitting in a class all day may make them uncomfortable. Experiential Learners take up about 5% of the population.
Mrs. Drake will incorporate movement into her lessons to help experiential learners. She does this through gallery walks and having students answer questions with information from stations inside the classroom and occasionally in the hallways.
Mrs. Willison includes STEM projects in some of her lessons to have hands-on activities. She might even assign choice board projects with different hands-on activities to add some variety.
“Young learners enjoy using Play-Doh to form letters or writing words or numbers in shaving cream. Lots of cutting, pasting, and movement with instruction is important when giving instruction to hands-on learners,” Willison said.
Even though the teachers both teach different grades, they teach students with certain learning styles in similar ways. For example, both teachers will use or give students charts and diagrams to help them visualize information. Both teachers will also include audio clips in their learning to help auditory learning students.
The teachers have differences in the ways they teach students with certain learning styles as well. When it comes to experiential learning, 3rd graders have more elements as they will not only have movement in their lessons, but they will also have shaving cream, playdoh and make things with glue and scissors to enhance their learning.
Zack Hudson, a Certified Professional in Talent Development (CPTD) since 2017, helps people get better at their jobs and teaches others how to do the same, based on their learning style. He currently works as the Director of Talent Management for Kindred at Home and Vice President of Strategic Partnership at the Atlanta Chapter of the Association of Talent Development.
“Experiential learning goes really heavily into younger grade levels. Because as you’re younger your attention span is a lot shorter and so you’ve got to experience the learning to really get a grasp of it. So that’s why you’ll see a lot of fun experiments and activities that they do and switching things up a lot because it’s about building a memorable experience that they can hold on to so then they can learn. So as you go up in grades it gets to be less than, as you get to middle school and high school certainly college, it becomes much less experiential and much more what we would call auditory so just where somebody is just talking and teaching as opposed to doing anything else. So, if someone is an experiential learner and they are struggling with learning then think about ways that you can turn that learning into an experience,” Hudson said about experiential learning throughout the learning system.
As teaching methods and the material in classes change, Students may start to not understand the material in their classes. To fix this, students can study and learn the material on their own based on their learning style in different ways.

Visual learners can look at their books, learning material or a YouTube video to help study and understand things. Audio learners can listen to the YouTube pieces, podcasts or get together with other students and listen to what they learned. Experiential learners could go to a study group, make an experience out of the learning material, find different ways to get hands-on learning or create a general experience to make a memory remember about the material.
Even though it may get harder for students with certain learning styles to understand concepts as they progress through school, they can always find different study methods and teachers to help them understand. Students can find out what learning style they have here. Whenever students do have trouble in class, they should always let their teacher know so then they can help the student with their needs.

Carmen Wilson • Nov 27, 2020 at 10:13 PM
Keep up the good work! I am so proud of you!