Alarming dangers of alarm clocks
November 15, 2018
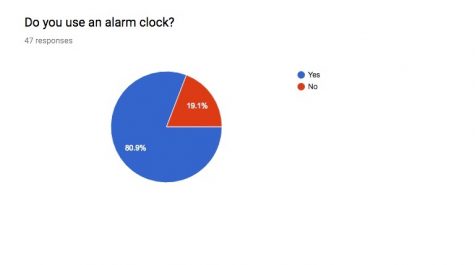
Almost all high school students awake to the blaring machine of death, also known as an alarm clock. Alarm clocks create a convenient way for individuals to easily wake up in the morning through the click of a button. These smartphone alarm clock apps play a crucial role in the life of a high school student, and in a survey given to NC students, 80.9% of students use their phones as an alarm clock to wake up in the morning. However, continuous use of alarm clocks show detrimental impacts to the health of both teens and adults.
The sleep cycle consists of five stages, with rapid eye movement (R.E.M) enabling the deepest sleep. Traditional alarm clocks do not determine which cycle a user wakes up in, causing an abrupt disruption in the sleep cycle and ultimately resulting in sleep deprivation among users. Long-term sleep deprivation leads to dangerous health issues among individuals.
While alarm clocks involve certain dangers to their users, they present a necessary evil to the changing and developing pace of society. Students should waste no time in removing these hazardous devices that show extensive damage to one’s health.

“After decades of research, the case can be confidently made that sleep loss and sleep disorders have profound and widespread effects on human health. They take a toll on nearly every key indicator of public health: mortality, morbidity, performance, accidents and injuries, functioning and quality of life, family well-being, and health care utilization,” Harvey R. Colten and Bruce M. Altevogt of The Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Sleep Medicine and Research said.
Along with causing disrupted sleep and irregular sleeping patterns among teens, alarm clocks provoke stress to the heart. The sudden ringing from the clocks causes strain to the heart by unexpectedly surprising users.
“Waking up abruptly can cause higher blood pressure and heart rate. Besides increasing your blood pressure, an alarm can add to your stress levels by getting your adrenaline rushing,” an ABC news article said.
The safety of using alarm clocks quickly changed as research revealed the dangers of the modern application.
Students typically rely on their smartphones to wake up every morning, but ironically, these devices can also pose a risk to the sleep schedules of teens. Despite the alarm clock’s known use for providing more sleep and ensuring the user a guaranteed wake up time, setting an alarm clock can throw the user into the depths of the Internet by the simple click of a notification.
Students that keep their phones next to them as they sleep tend to stay on their devices longer and later. The smartphones display bright lights, which creates further dangers for users.
“Not only does it fill your mind with more things to process but studies have shown that blue light (the type of light your phone emits) can lead to insomnia and depression….our brain can interpret the light from phones as sunlight which stops us from producing melatonin (a sleep hormone) and urges our body to ‘keep going’ because it’s ‘not time to sleep,’” writer for the Matthew Thompson Blogs Matthew Thompson said.
These hand-held luminescent devices display tempting notifications, luring users into deep conversations during the vital hours of sleep and causing these teens to stay awake. Eventually, teens end up trading in sleep for a text message.
“Sometimes, if someone texts me right before, then I usually answer if [the message] is urgent,” sophomore Katie Hines said.
The non-REM sleeping stage includes the lightest phase of sleep. Modern applications can sense a user’s sleeping pattern and locate the lighter stage of the sleeping period, allowing the user to wake up naturally and feel re-energized.
Individuals may also take further steps to wake up without feeling tired. Students may try sleeping and waking up without the use of an alarm clock. This non binding method lets users understand their sleeping habits without an alarm and allows them to discover the times their bodies naturally wake up and what time is best for them. This process requires more flexibility and will help users identify their personal sleeping schedules and adjust how they sleep in the future.
Unfortunately, students with strict schedules experience trouble adhering to a looser arrangement away from the use of alarm clocks. However, applications such as Sleep Cycle remain readily available to users with the touch of a finger and help maintain sleep patterns.
Despite the concealed dangers of using alarm clocks, there remains safer ways to wake up without damages to one’s health.







